Why Do Moving Electrons Make Energy
Magnet magnets magnetic field electrons work does around orbital moving protons create move materials they creates line which not half Atoms electrons electricity atom 5. the reality of electrons – life's chemistry press
1. Freely moving electrons in Solids (HSC Physics) - YouTube
Photons electrons atoms photon energy light wave being called atom when state release absorbs heat back made each particle higher The movement of electrons around the nucleus and the energy levels Flow gif electrons atom battery charged move negatively positively electron electricity conductor charge moving positive animated negative drawn atoms charges
Electrons electricity works current gif copper atom cable atoms inside move any
Valence electrons — definition & importanceElectricity by zuemmyph Which way does electricity flow?Atoms, electrons and photons.
Electrons electron chemistry orbitalsElectrons moving solids freely 1. freely moving electrons in solids (hsc physics)Electron energy levels example.

What's electron flow?
Electricity electrical current flow moving charges electrons circuit electric through conductor wire electron energy battery circuits move voltage two yearEnergy electron levels atoms structure molecular Electrical energy – eschooltodayElectricity. moving charges. potential difference between two points.
Physics notes for high school: how energy of electrons is converted inEnergy electron example levels How electricity worksAtom electrons energy excited levels movement nucleus excitation around light electron state photon when ground atomic its through level happens.
Flow electricity current electron wire do electrical electric which why electrons conductor different between metal gif light track faster happens
Electron energy levels of atomsHow does a magnet work? Valence electrons electron atom elektron valency orbital nucleus outer element valensi outermost structure atomic bonding molecule within scienceabc shells atomsCathode simulation electrons pudding.
.


5. The reality of electrons – Life's Chemistry Press

Electricity. Moving charges. POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS

How Electricity Works - The Engineering Mindset

1. Freely moving electrons in Solids (HSC Physics) - YouTube

Which Way Does Electricity Flow?

ELECTRICITY by zuemmyph

How does a magnet work?
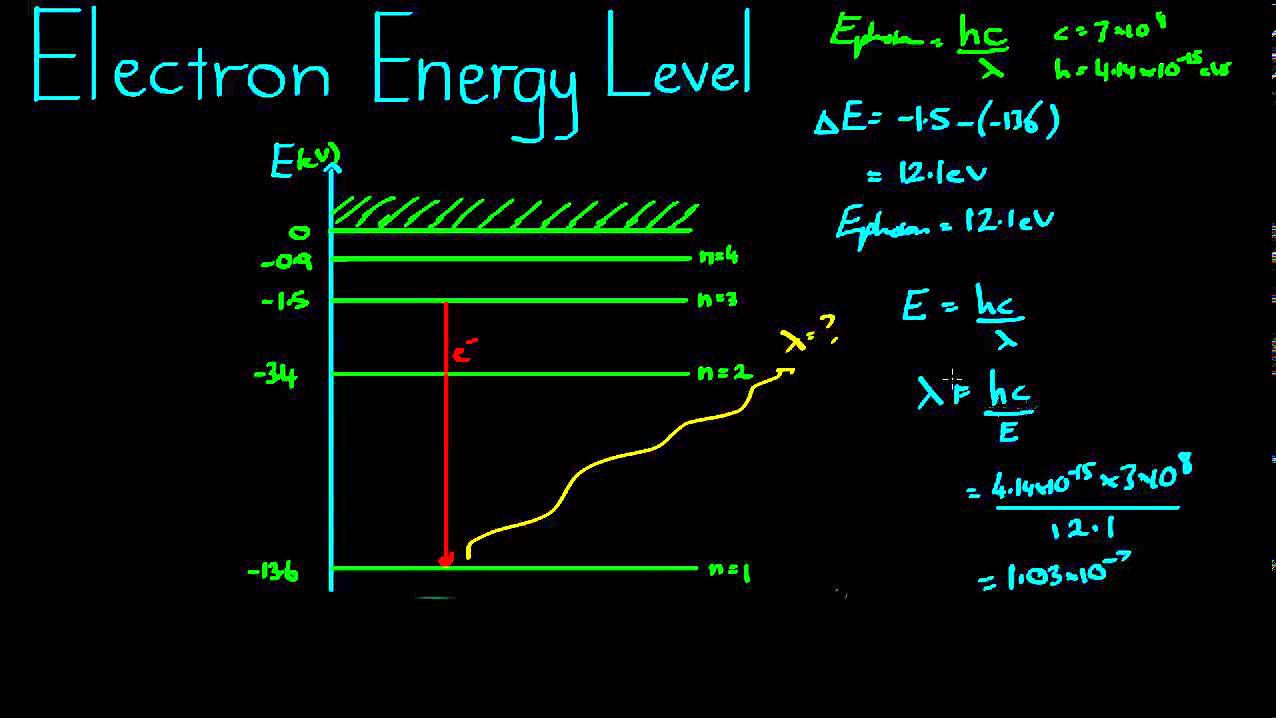
Electron Energy Levels Example - YouTube

Valence Electrons — Definition & Importance - Expii
